Dynamic KGs vs. Temporal KGs
这篇文章我也有放在medium上。
Temporal Knowledge Graph
The temporal knowledge graph is a special type of knowledge graph. Usually, knowledge graph data is presented in the form of triples, which can be denoted as (h, r, t) where h, r and t are the abbreviations of head entity, relation, and tail entity respectively. In temporal knowledge graph, in addition to entities and relations, the temporal attribute of relations is included as well. Temporal knowledge graph data is presented in the form of quadruples, which are denoted as (h, r, t, a_t) where a_t is the temporal attribute on relations. For instance, (Trump, is_president_of, US, 2017–2020).
Representation learning methods on temporal knowledge graphs are usually derived from the methods on usual knowledge graphs that are in triple form. For example, TransE-TAE model is designed based on TransE model.
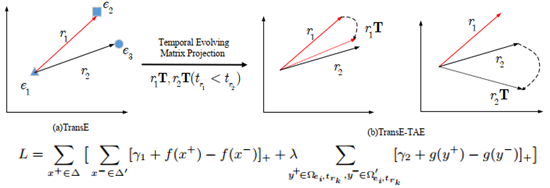
Temporal knowledge graph embedding methods usually learn embeddings of timestamps or time spans by inserting the temporal variable into the score function when training. After the training process is finished, embeddings of all entities, relations and temporal attributes are generated.
The experiment tasks conducted on temporal knowledge graph mainly are link prediction and temporal information prediction. The link prediction task includes entity prediction and relation prediction, which are also the basic tasks on triple-form knowledge graph embedding. Formally, link prediction tasks can be denoted as (?, r, t, a_t), (h, r, ?, a_t) or (h, ?, t, a_t). The temporal information task aims to predict the timestamp or time span when a given event (triple) happened. Likewise, this task can be denoted as (h, r, t, ?). Latest studies on temporal knowledge graph are able to predict future events.
Dynamic Knowledge Graph
The dynamic knowledge graph is also called the evolving knowledge graph, where the topological structure or attributive information is changing over time. Considering that the alteration of attributes on entities and relations is usually trivial, the studies on dynamic knowledge graph generally focus on non-attributive knowledge graph and its topological structure. Frankly speaking, the topological alteration means the addition or deletion of entities and relations.
By far, the study on dynamics on knowledge graph is still under-explored. Most of the existing studies on such topic only consider such a scenario that new entities are emerging. One apparent reason for this is the peculiarity of the knowledge graph. The in-store triples in a knowledge graph are usually immutable facts from the real world, which makes the deletion of existing entities and relations hardly happen. Besides, the amount of relation types is relatively limited compared to the enormous amount of entity types, making the emergence of new relation sporadical. There are some alternative names for emerging entities, such as out-of-sample entities and unseen entities.
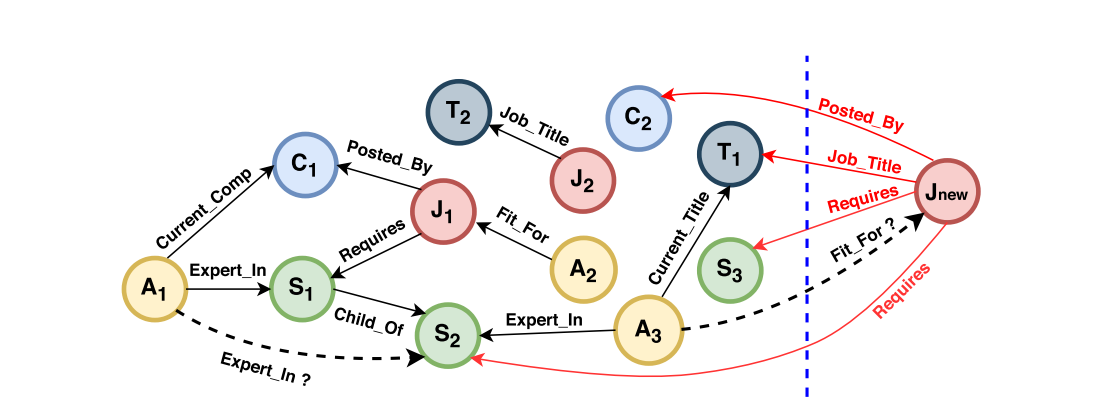
Differences
- The data of temporal knowledge graph is in form of quadruple, while dynamic knowledge graph embedding mainly focuses on non-attributive triple data.
- Temporal knowledge graph embedding methods are trained on stationary datasets. Dynamic knowledge graph embedding methods are designed and trained on evolving datasets.
- Temporal knowledge graph embedding learns embeddings of temporal attributes and can predict temporal information for events. Dynamic knowledge graph embedding aims to learn the embeddings of emerging entities and relations (and may modify the embeddings of existing entities and relations) to predict the links between emerging entities and existing entities.